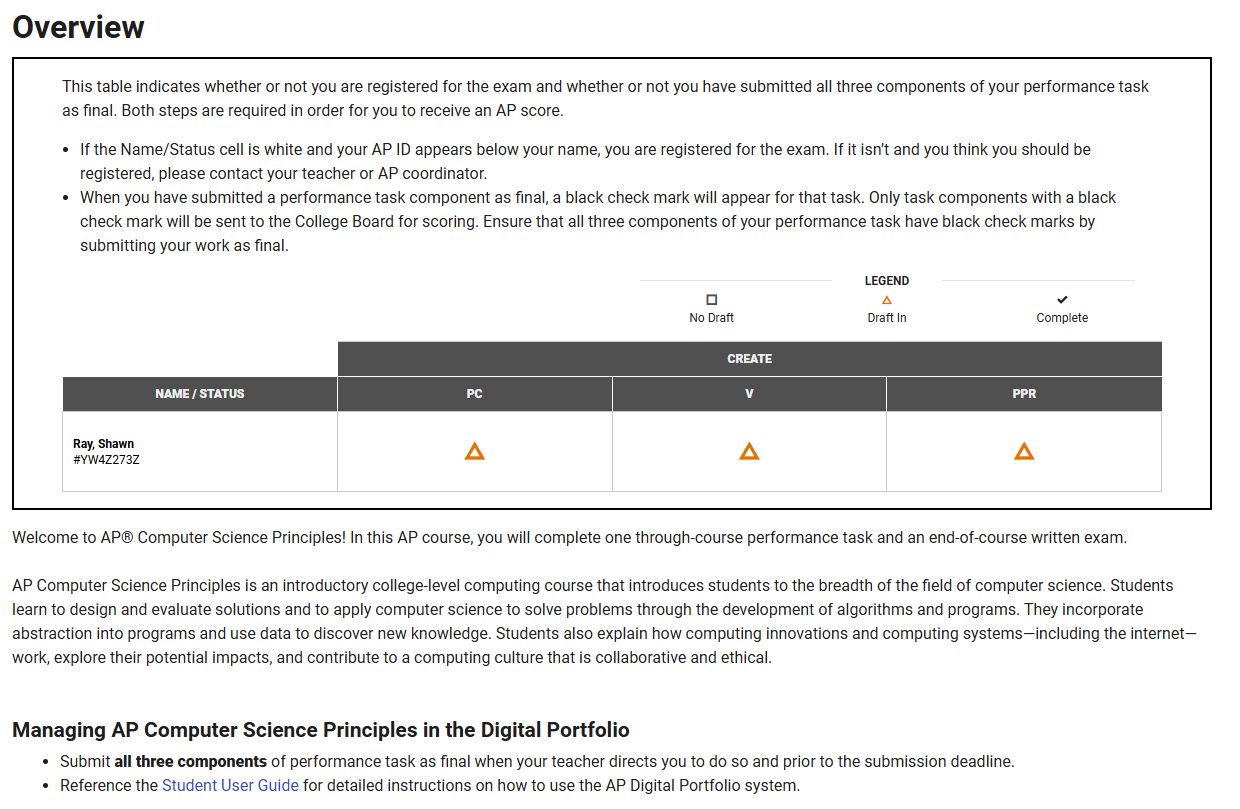
Overview of PC, Video, and PPR
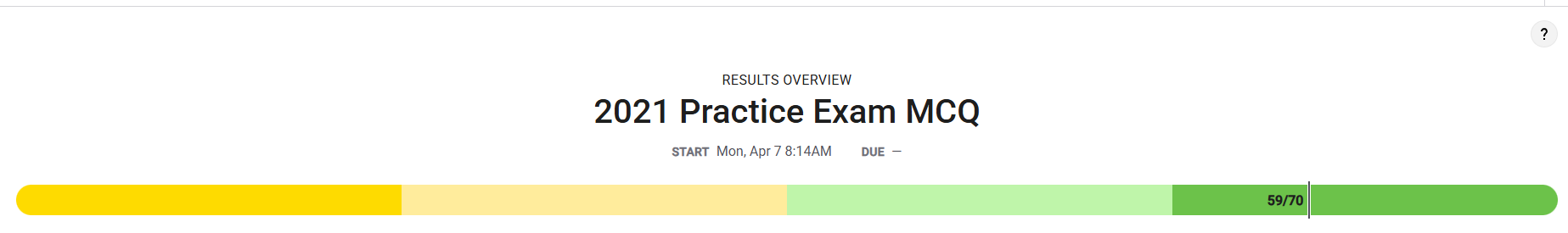
MCQ Overview
MCQ Topics
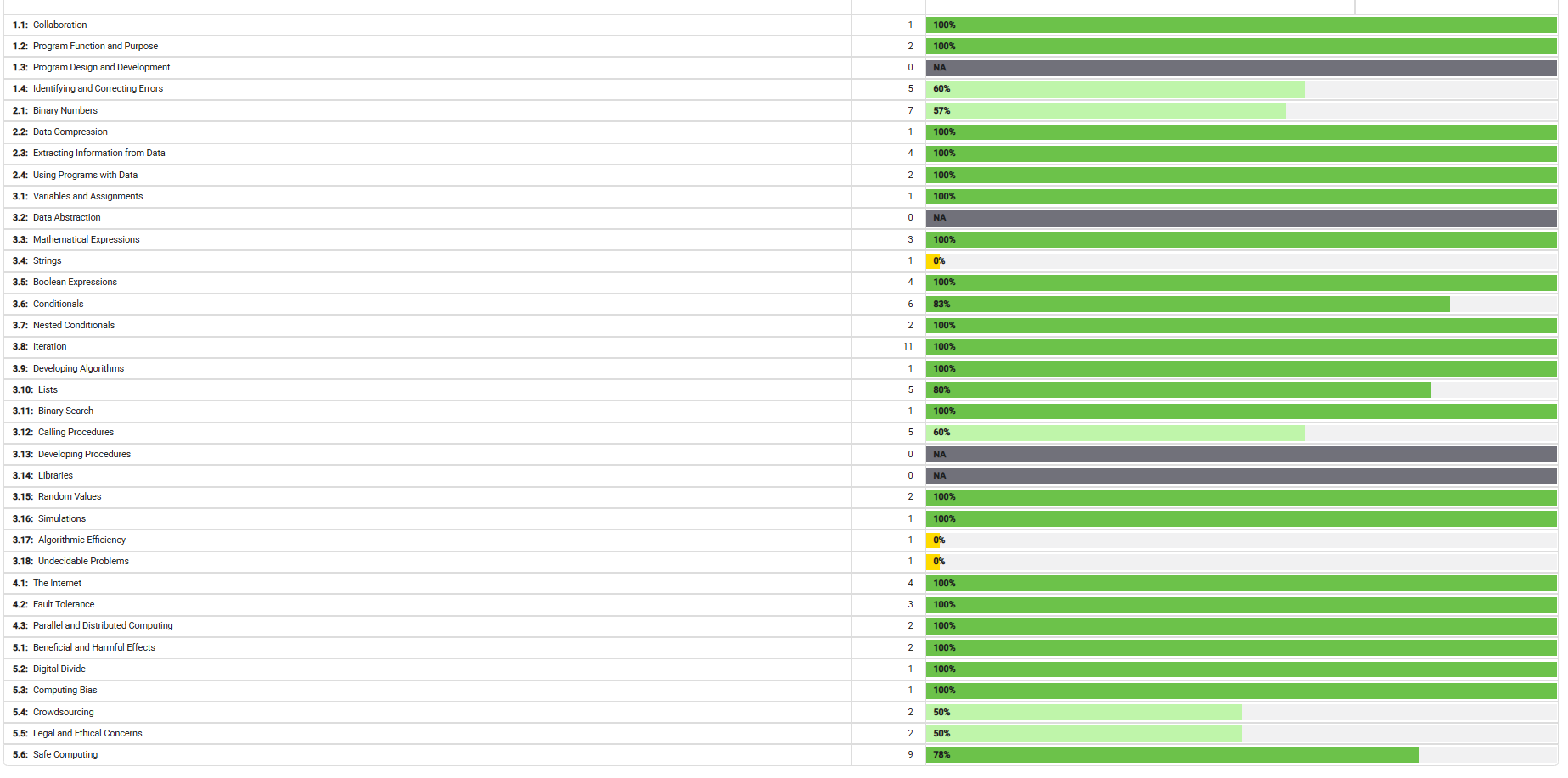
Strengths (100%)
| Topic | Section |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | 1.1 |
| Program Function and Purpose | 1.2 |
| Data Compression | 2.2 |
| Extracting Information from Data | 2.3 |
| Using Programs with Data | 2.4 |
| Variables and Assignments | 3.1 |
| Mathematical Expressions | 3.3 |
| Boolean Expressions | 3.5 |
| Nested Conditionals | 3.7 |
| Iteration | 3.8 |
| Developing Algorithms | 3.9 |
| Binary Search | 3.11 |
| Random Values | 3.15 |
| Simulations | 3.16 |
| The Internet | 4.1 |
| Fault Tolerance | 4.2 |
| Parallel and Distributed Computing | 4.3 |
| Beneficial and Harmful Effects | 5.1 |
| Digital Divide | 5.2 |
| Computing Bias | 5.3 |
Moderate Areas (50-83%)
| Topic | Section | Mastery |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying and Correcting Errors | 1.4 | 60% |
| Binary Numbers | 2.1 | 57% |
| Conditionals | 3.6 | 83% |
| Lists | 3.10 | 80% |
| Calling Procedures | 3.12 | 60% |
| Safe Computing | 5.6 | 78% |
| Crowdsourcing | 5.4 | 50% |
| Legal and Ethical Concerns | 5.5 | 50% |
Weaknesses/Not Applicable (0%)
| Topic | Section | Mastery |
|---|---|---|
| Program Design and Development | 1.3 | NA |
| Data Abstraction | 3.2 | NA |
| Strings | 3.4 | 0% |
| Developing Procedures | 3.13 | NA |
| Libraries | 3.14 | NA |
| Algorithmic Efficiency | 3.17 | 0% |
| Undecidable Problems | 3.18 | 0% |
Lesson Reviews
| Topic | Section | Mastery | Lesson |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strings | 3.4 | 0% | Link |
| Algorithmic Efficiency (L) | 3.17 | 0% | Link |
| Undecidable Problems (L) | 3.18 | 0% | Link |
| Identifying and Correcting Errors | 1.4 | 60% | YouTube, AP Classroom |
| Binary Numbers | 2.1 | 57% | AP Classroom |
| Conditionals | 3.6 | 83% | Link |
| Lists | 3.10 | 80% | Link |
| Calling Procedures | 3.12 | 60% | AP Classroom |
| Safe Computing | 5.6 | 78% | Link |
| Crowdsourcing | 5.4 | 50% | Link |
| Legal and Ethical Concerns | 5.5 | 50% | Link |
Big Idea 1: Creative Development
-
1.1 Collaboration
Working together improves problem-solving and program design. -
1.2 Program Function and Purpose
Programs are written to solve problems, express creativity, or perform tasks. -
1.3 Program Design and Development
Plan before coding: pseudocode, design steps, and test cases matter. -
1.4 Identifying and Correcting Errors
Debugging is key — spot, fix, and explain errors in logic or syntax.
Big Idea 2: Data
-
2.1 Binary Numbers
All digital data is stored using 0s and 1s — binary is the base of computing. -
2.2 Data Compression
Reduce file size while preserving information (lossless vs lossy). -
2.3 Extracting Information from Data
Use patterns, filtering, and visualizations to gain insight. -
2.4 Using Programs with Data
Programs can process and transform data sets to reveal meaning. -
2.5 Legal and Ethical Concerns
Consider privacy, security, and bias in how data is used.
Big Idea 3: Algorithms and Programming
-
3.1 Variables and Assignments
Store data using variables that can change over time. -
3.2 Data Abstraction
Use lists or other structures to manage related data efficiently. -
3.3 Mathematical Expressions
Use math operators to process data and logic. -
3.4 Strings
Strings are sequences of characters — they can be split, combined, and more. -
3.5 Boolean Expressions
Usetrue/falselogic to make decisions. -
3.6 Conditionals
If/else logic lets programs choose between actions. -
3.7 Iteration
Loops (likeforandwhile) repeat actions to simplify code. -
3.8-3.9 Lists
Store multiple values in one place; manipulate them efficiently. -
3.10-3.11 Traversing Lists
Use loops to access and change list values. -
3.12 Calling Procedures
Run a set of instructions by calling a defined procedure or function. -
3.13 Developing Procedures
Write reusable code blocks to organize and simplify tasks. -
3.14 Libraries
Use external code to save time and reduce errors. -
3.15-3.16 Simulations
Imitate real-world systems for testing and analysis. -
3.17 Algorithmic Efficiency
Measure how fast or efficient your algorithm is. -
3.18 Undecidable Problems
Some problems can’t be solved by any algorithm — they’re undecidable.
Big Idea 4: Computing Systems and Networks
-
4.1 The Internet
A network of networks — enables global communication. -
4.2 Fault Tolerance
Internet systems can reroute data to handle errors or failures.
Big Idea 5: Impact of Computing
-
5.1 Computing Innovations
Tech changes the world — socially, ethically, and practically. -
5.2 Effects of Computing
Includes both positive and negative impacts on society and individuals. -
5.3 Crowdsourcing
Gather data or solve problems by tapping into large groups of people. -
5.4 Legal and Ethical Concerns
Think about ownership, security, and equity in digital innovations. -
5.5 Safe Computing
Protect data with passwords, encryption, and smart digital habits. -
5.6 Cybersecurity
Understand threats like viruses and strategies like firewalls.
Plan of Study
1. Procedure Mastery
- Topics: Developing Procedures (3.13), Calling Procedures (3.12), Libraries (3.14)
- Actions:
- Write multiple functions from scratch
- Refactor an old project to use more custom procedures
- Practice importing and using
math,random, anddatetimelibraries
2. Algorithm & Logic Precision
- Topics: Algorithmic Efficiency (3.17), Binary Numbers (2.1), Boolean & Nested Conditionals
- Actions:
- Study sorting/searching concepts (linear vs binary)
- Solve logic puzzles using
if,elif, andelse - Break down time complexity in one of my Python projects
3. Debugging Practice
- Topic: Identifying and Correcting Errors (1.4)
- Actions:
- Analyze code snippets with errors (intentional bugs)
- Build a short buggy program and fix it line-by-line
- Peer review or swap code for external debugging
Targeted Practice Tasks
- Write a recursive function and explain the base case
- Create a list-based project (like a leaderboard or to-do app)
- Simulate a real-world process using iteration & conditionals (e.g., vending machine, dice game)
- Practice decoding binary manually, then write a converter
- Take random CSP question sets (Quizizz, AP Classroom)
Creative Challenges (Apply What You Know)
- String Remix: Build a string editor that lets users input text and apply transformations (reverse, capitalize, replace).
- Binary Guessing Game: Code a game where users guess the decimal value of a binary number.
- Algorithm Race: Write two sorting algorithms, time them, and visualize results.
- “Bug Hunter” Blog Post: Document a debugging process in detail — what went wrong, how you diagnosed it, what you learned.
- CS + You: Visualize how you use algorithms or data daily (recommendations, search, GPS, etc.).
Video Playlist
A mix of quick refreshers and deeper dives:
- Big O Notation Explained
- String Manipulation in Python
- AP CSP Boolean Logic Review
- Intro to Binary Numbers
- Undecidable Problems in CS
Final Strategy Notes
- Focus most on sections that need the most improvement
- Use active learning: coding, drawing, teaching
- Track progress weekly in a Google Doc or journal
- Schedule full-length AP practice test after completing the study blocks
- Khan Academy
- Collegeboard Videos
- Peer Reviews
- Youtube Videos