Introduction
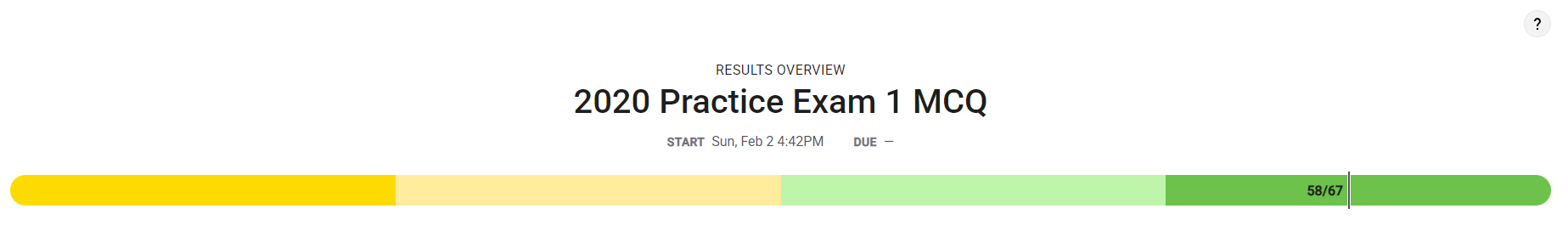
The 2020 MCQ for CSP on the College Board exam tests your knowledge in computer science. It includes 70 questions covering topics like programming, algorithms, data structures, and the internet.
Needs Improvement
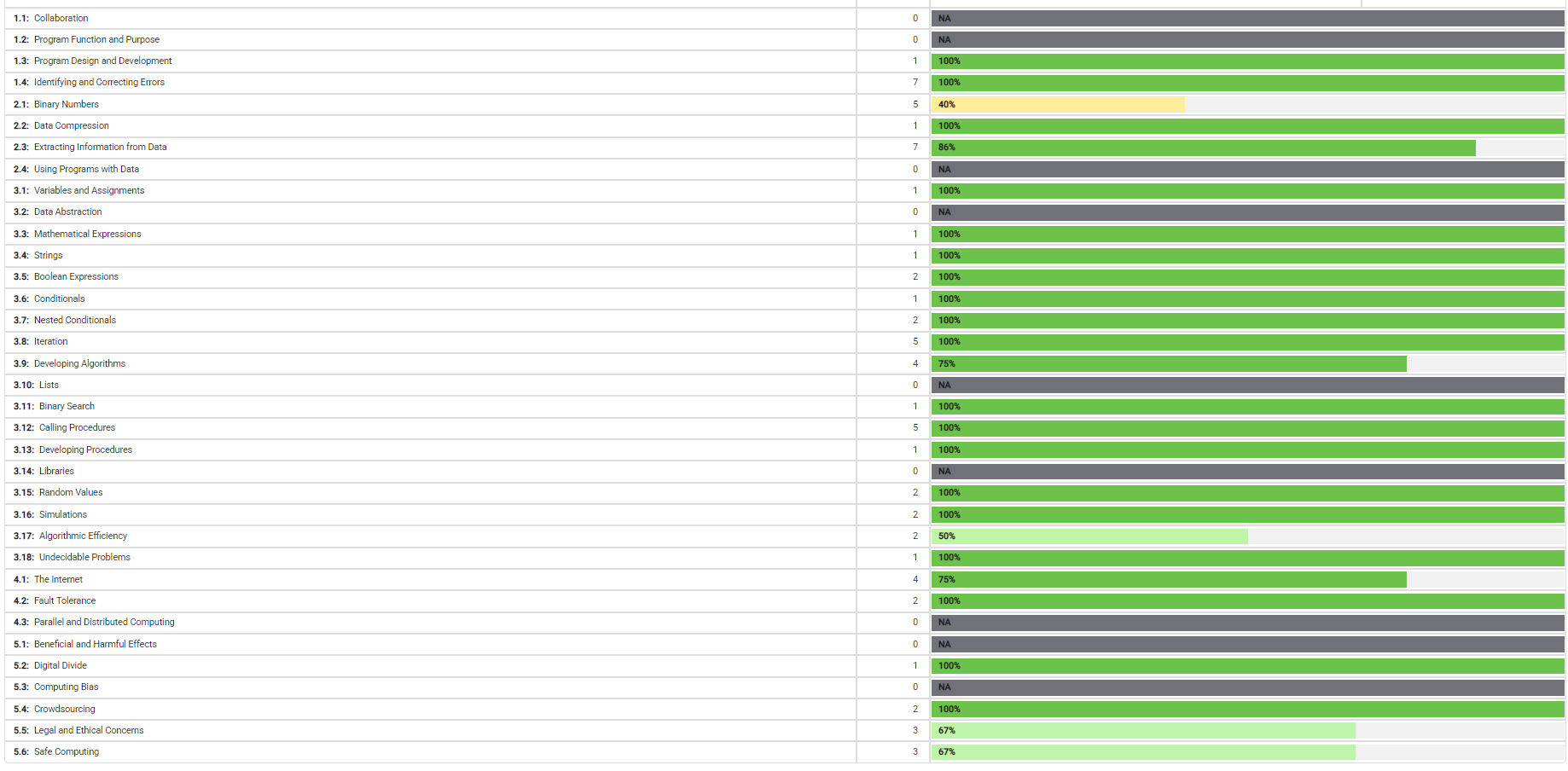
- Binary Numbers
- Developing Algorithms
- Algorithmic Efficiency
- Legal and Ethical Concerns
- Safe Computing
Comparing to Last MCQ
Improvements
- Lists
- Calling Procedures
- Developing Procedures
- Algorithmic Efficiency (Still Needs Work)
- Beneficial and Harmful Effects
Corrections
Question 4

Initial Thoughts:
I thought the error might be due to an undecidable problem or rounding errors with floating-point numbers. But I wasn’t sure about how overflow actually happens with integers.
Correction:
The error occurs because the program is trying to add two numbers that are too large for the number of bits it uses to represent integers. The correct answer is C: “The program can only use a fixed number of bits to represent integers; the computed sum is greater than the maximum representable value.” This is what causes an overflow error.
Question 11
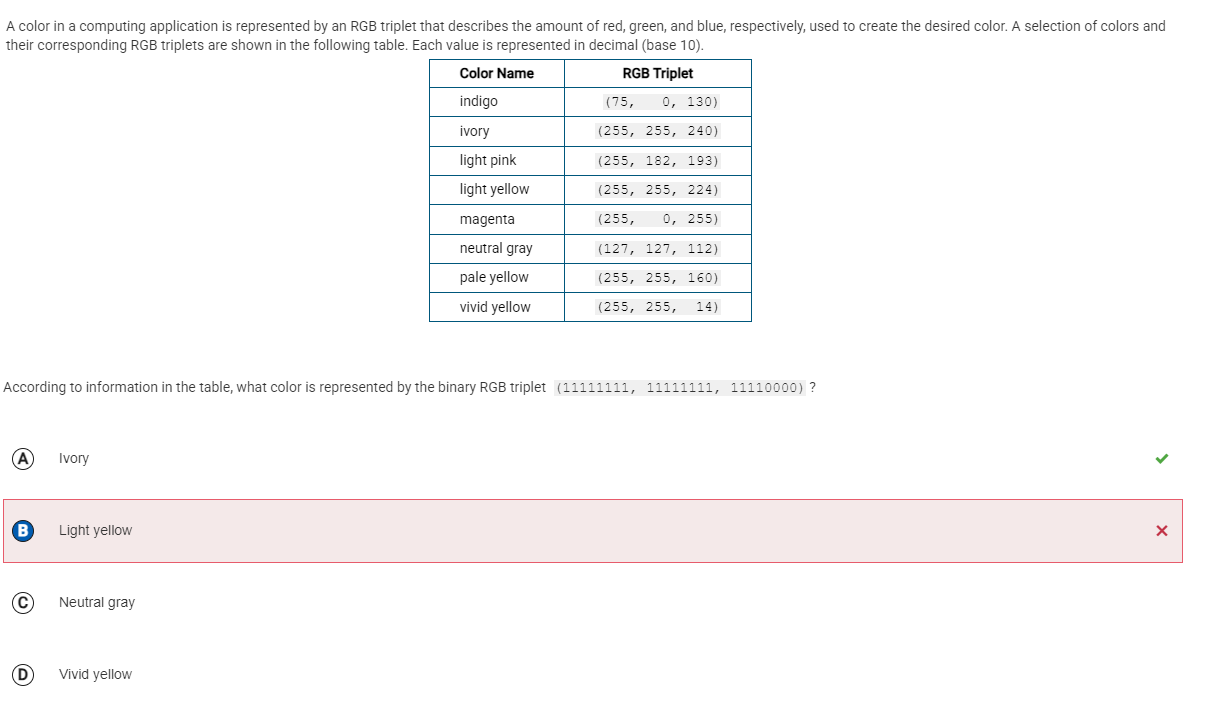
Initial Thoughts:
I noticed that the triplet is in binary, so I need to convert each of the binary numbers to decimal to match it with one of the colors in the table. I can then compare the result to the RGB values in the table.
Correction:
First, convert each binary number in the triplet to decimal:
- 11111111 (binary) = 255 (decimal)
- 11111111 (binary) = 255 (decimal)
- 11110000 (binary) = 240 (decimal) So the RGB triplet is (255, 255, 240), which matches ivory in the table.
Therefore, the color represented by the binary RGB triplet (11111111, 11111111, 11110000) is ivory.
Question 23
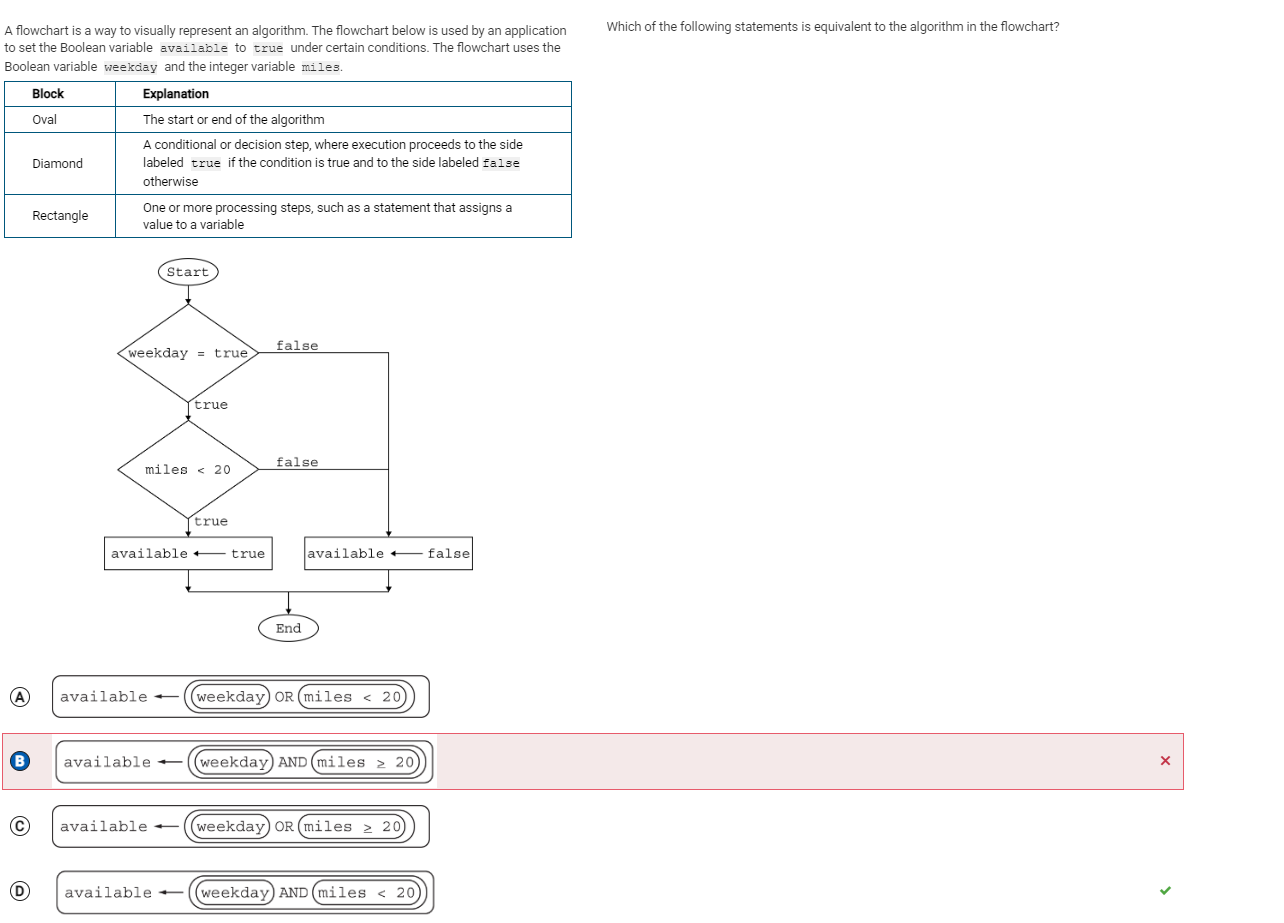
Initial Thoughts:
I honestly do not know how I got this wrong, I think this was a mouse slip or just a simple mistake
Corrections:
No crazy corrections, just be more careful and look out next time.
Question 25
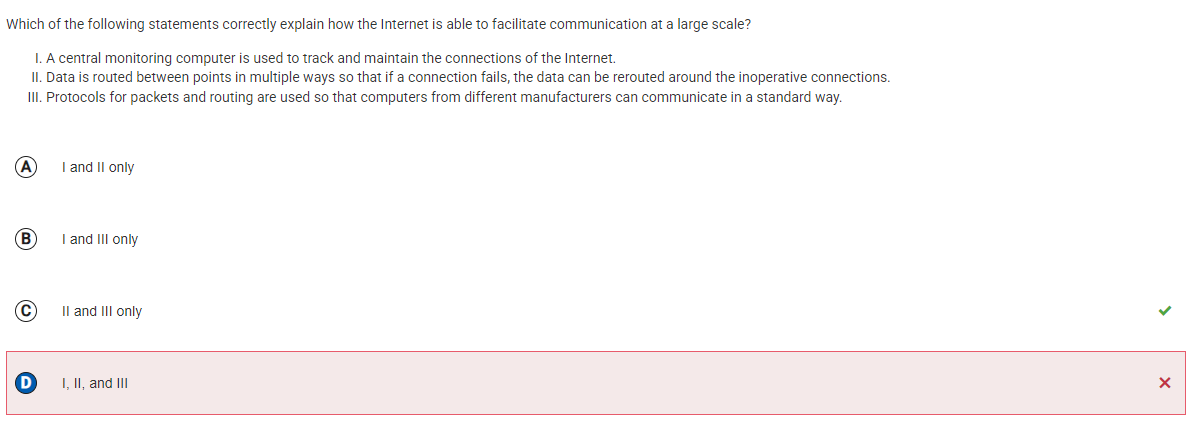
Initial Thoughts:
I thought the Internet’s communication system worked with a central computer monitoring everything and managing connections.
Corrections: C (II and III only) - The Internet routes data through multiple paths to ensure it can still work if one route fails, and protocols like TCP/IP allow different computers to communicate in a standard way.
Question 26
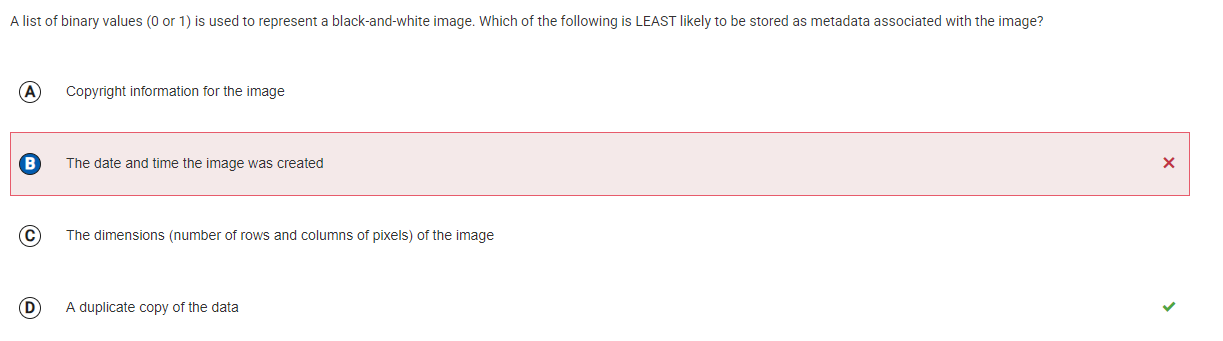
Initial Thoughts:
I thought metadata would typically include information like copyright, date/time, and image dimensions, but a duplicate copy of the data seemed unnecessary as metadata.
Correction:
D (A duplicate copy of the data) - Metadata usually includes details like copyright, creation date, and dimensions, but a duplicate of the image data itself is not considered metadata.
Question 40
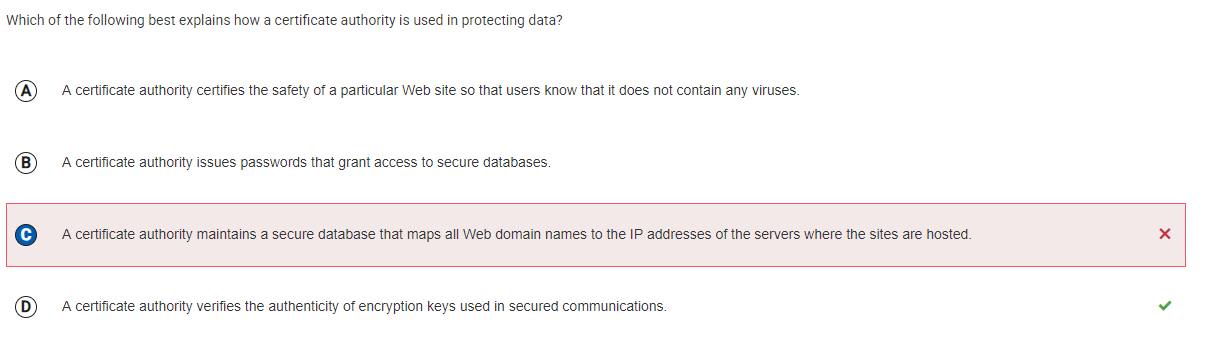
Initial Thoughts: I thought a certificate authority might help with security in general, like granting access to databases or verifying website safety, but I wasn’t sure exactly how it worked in terms of encryption.
Corrections: D (A certificate authority verifies the authenticity of encryption keys used in secured communications). A certificate authority (CA) does not deal with things like granting access or mapping IP addresses. Instead, it ensures that encryption keys used for secure communications are authentic, helping verify that the data exchanged is protected from tampering. This is crucial for establishing secure connections, like HTTPS for websites.
Question 49
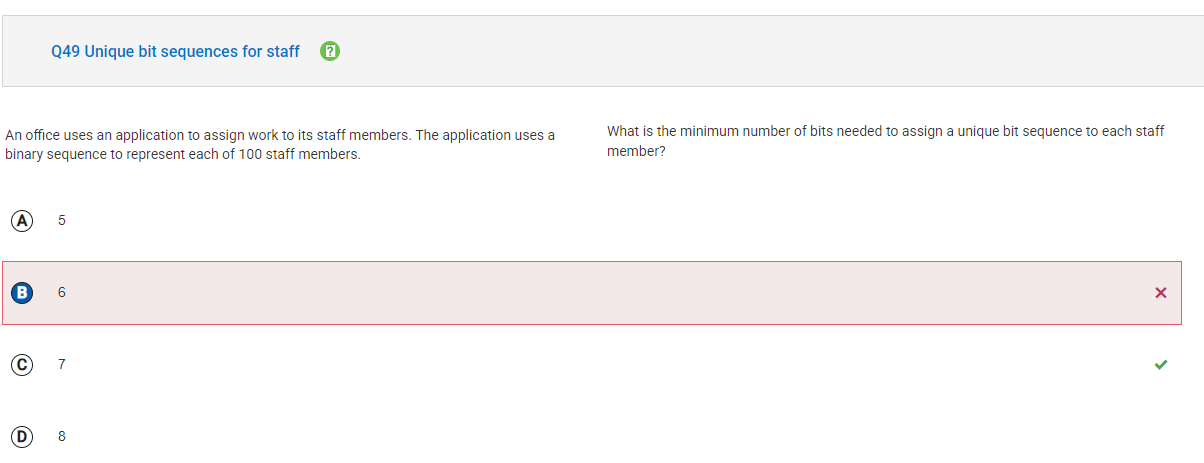
Initial Thoughts: I figured that since we’re dealing with 100 staff members, I would need a number of bits that can represent at least 100 different values. I know that 2^n gives the number of unique values that can be represented by n bits.
Correct Answer: B (6)
Corrections: The minimum number of bits needed to assign a unique sequence to each of the 100 staff members is 6 bits because 2^6 = 64, which is not enough, but 2^7 = 128, which is more than enough to represent 100 staff members. Therefore, 7 bits are technically enough, but since the question asks for the minimum, 6 is the right answer.
Question 50
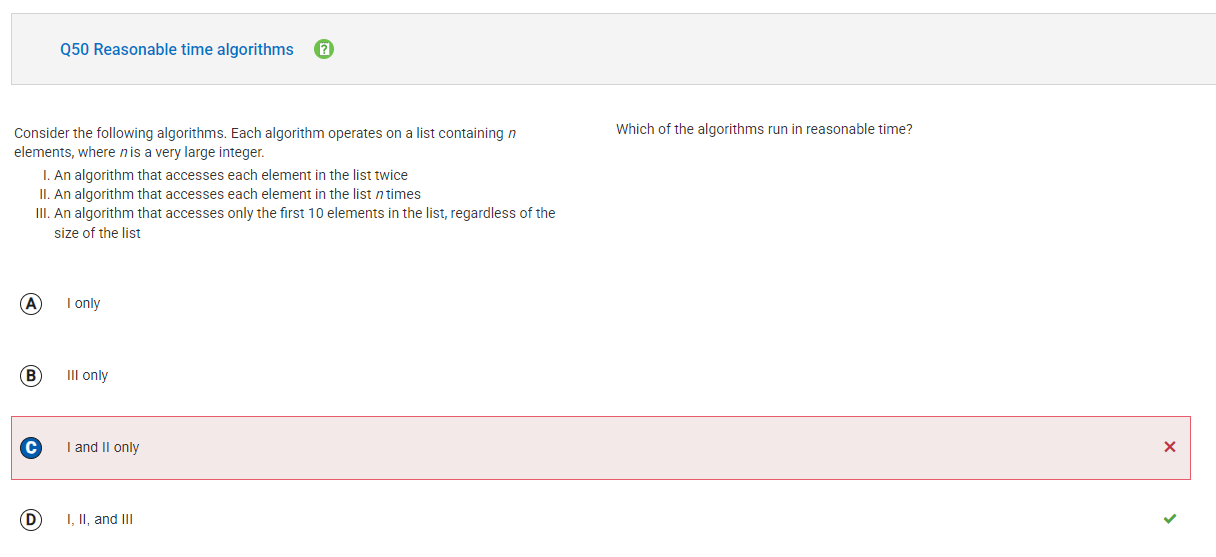
Initial Thoughts: I know that algorithm efficiency depends on how the size of the input (n) impacts its execution time. The more times an algorithm accesses elements, the longer it will take. I should consider how the size of n affects each case.
Correct Answer: D (I, II, and III)
Corrections:
- Algorithm I accesses each element twice, so it runs in O(2n) time, which is still O(n) (since constants don’t matter in big-O notation). It will run in a reasonable time.
- Algorithm II accesses each element n times, so it runs in O(n²), but for very large n, this can still be considered reasonable for some cases (depending on implementation, hardware, etc.).
- Algorithm III accesses only the first 10 elements, regardless of the size of n. It runs in O(10) time, which is constant and always runs in a reasonable time, no matter the size of n. Since all the algorithms run in reasonable time under typical conditions, the correct answer is D.
Question 51

Initial Thoughts: Creative Commons is a licensing system that allows creators to specify how others can use and distribute their work. It’s not about transmission of messages or security, but rather how content can be shared or used legally.
Correct Answer: A (Creative Commons gives creators of digital content the ability to indicate how their works can be legally used and distributed, enabling broad access to digital information.)
Corrections:
- Option A correctly explains that Creative Commons is about allowing creators to specify the terms under which others can use their works, facilitating legal sharing and broad access.
- Option B is incorrect because Creative Commons doesn’t give users the right to use any copyrighted work; it only applies to works that the creators have explicitly licensed under Creative Commons.
- Option C is about data transmission, which is unrelated to Creative Commons.
- Option D is about private transmission, which doesn’t relate to Creative Commons either.
The correct answer is A because it directly addresses how Creative Commons works in terms of content licensing.