Computing Bias Lesson 🧠
Introduction 📌
Computing bias occurs when computer systems systematically and unfairly discriminate against certain groups. Bias in computing can reinforce social inequalities, create unfair advantages, and lead to real-world harm. This lesson explores how bias emerges, real-world examples, and strategies for mitigation.
What is Computing Bias?
“We can say that a computer system is biased if it both unfairly and systematically discriminates against one group in favor of another.” – Nissenbaum et al. (Cornell Paper)

Doctor or Nurse Drawings 🎨
Types of Bias in Computing 🔍
Pre-existing Social Bias
- Originates from societal norms, stereotypes, or historical inequalities.
- Embedded into technology due to biased data, biased creators, or societal influence.
- Examples:
- Hiring algorithms favoring men over women.
- Facial recognition systems performing poorly on non-white faces.
Technical Bias
- Stems from design, implementation, or structural limitations in technology.
- Even systems built with good intentions may introduce bias through their function.
- Examples:
- Google Translate assigning gendered pronouns based on stereotypes.
- Default settings not representing all user demographics.
Emergent Social Bias
- Develops over time as a system interacts with users or adapts to real-world data.
- AI models may evolve in a biased manner based on user interactions.
- Examples:
- AI chatbots learning harmful language from users.
- Search engines amplifying biased content over time.

Question 1: ❓
A company implements an AI hiring system that unintentionally prefers male candidates over female candidates because it was trained on past hiring data from a male-dominated industry. What type of bias is this an example of?
- A) Pre-existing Social Bias
- B) Technical Bias
- C) Emergent Social Bias
- D) No Bias Present
Reveal Answer
Answer: A) Pre-existing Social Bias This bias originates from societal inequalities reflected in historical hiring data.Question 2: ❓
An AI-powered chatbot gradually starts using offensive language after interacting with online users who repeatedly expose it to toxic content. What type of bias does this represent?
- A) Pre-existing Social Bias
- B) Technical Bias
- C) Emergent Social Bias
- D) Algorithmic Efficiency Bias
Reveal Answer
Answer: C) Emergent Social Bias The chatbot learns bias over time from user interactions, rather than being biased from the start.Explicit Data vs. Implicit Data in Computing Bias 🧩
When analyzing how bias appears in computing, it’s important to understand the difference between explicit data and implicit data—both of which can influence biased outcomes.
Explicit Data 📊
- Data that is directly provided by users or systems.
- Clearly stated, structured, and intentional.
- Examples:
- Age, gender, and location entered in a form.
- A user rating a restaurant as 5 stars.
- A survey response about preferences.
Implicit Data 🔍
- Data that is collected indirectly based on user behavior or interactions.
- Often inferred through machine learning algorithms.
- Examples:
- Websites you visit frequently.
- Time spent on a particular video or article.
- The words you use in online searches.
How Does This Relate to Bias? ⚖️
Bias can emerge when implicit data is used in ways that reinforce stereotypes or favor certain groups unfairly. Since implicit data is often inferred, it can exaggerate trends and introduce bias unintentionally.
For example:
- Hiring AI Bias: If an AI hiring system learns from past implicit data (e.g., past hiring patterns favoring men), it may unknowingly downgrade female candidates, even if their explicit qualifications are the same.
- Search Engine Bias: If a search engine prioritizes implicit data (like what users click on the most), it might keep recommending biased results, reinforcing stereotypes.
Popcorn Hack #1:
Think of a real-world example where a computer system has shown bias. It could be something you’ve read about, experienced, or imagined.
Question:
Describe the biased system, explain what type of bias it represents (Pre-existing Social Bias, Technical Bias, or Emergent Social Bias), and suggest one way to reduce or fix the bias.
Example Response
"A facial recognition system fails to accurately recognize darker-skinned individuals. This is an example of **Technical Bias** because the training data lacked enough diversity. A way to fix this could be to ensure the dataset includes a wide range of skin tones before training the model."*Real-World Examples of Computing Bias 🌍
Amazon’s AI Hiring Tool
- Bias Type: Pre-existing Social Bias
- Amazon’s AI recruitment system favored male candidates due to past hiring data.
- The system penalized resumes with words like “women” (e.g., “Women’s Chess Club”).
- Impact: Women were unfairly ranked lower for job opportunities.
🔗 Read More
Google Translate Gender Bias
- Bias Type: Technical Bias
- When translating from gender-neutral languages, it introduced gender assumptions.
- Example:
- Turkish: O bir doktor → English: He is a doctor
- Turkish: O bir hemşire → English: She is a nurse
- Impact: Reinforced stereotypes about professions.
🔗 Read More
Microsoft’s AI Chatbot Tay
- Bias Type: Emergent Social Bias
- Tay learned from Twitter interactions but was manipulated into tweeting racist and offensive content within 24 hours.
- Impact: AI can absorb and amplify human biases without proper safeguards.
🔗 Read More
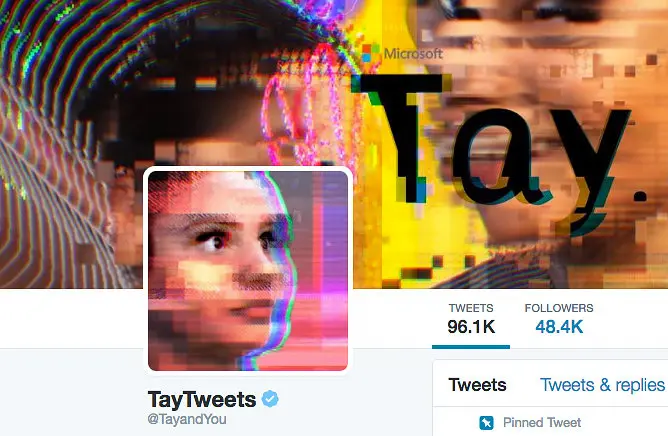
How to Mitigate these Biases?
Pre-existing Social Biases
- Bias Awareness Training: Educate developers to recognize and address social biases in design and data collection.
- Inclusive Design: Involve diverse perspectives in algorithm design to reflect multiple viewpoints.
- Bias Mitigation in Data Collection: Regularly audit and balance data to avoid harmful stereotypes.
Technical Bias
- Transparent Algorithms: Ensure algorithms are explainable and understandable to identify bias.
- Bias Testing and Auditing: Continuously test for fairness across demographics.
- Improved Evaluation Metrics: Use fairness-aware metrics to evaluate models and prevent group disadvantages.
Emergent Social Bias
- Human Oversight and Feedback Loops: Implement real-time monitoring and feedback from diverse users to correct emergent biases.
- User Moderation and Controls: Enable users to flag harmful content, reducing bias amplification.
- Algorithmic Accountability: Adapt algorithms to evolving social norms and continuously adjust based on feedback.
Popcorn Hack #2:
Bias in computing can lead to unfair outcomes, but there are ways to reduce it
Question:
In the financial industry, an AI system used to approve loan applications unintentionally favors male applicants over female applicants because it was trained on past loan approval data, which reflected gender biases. This is an example of Pre-existing Social Bias.
Give two ways to mitigate this bias and make the system more fair.
Example Responses
A music app recommends only popular songs and ignores lesser-known artists. - 1️⃣ **Add more variety** to the recommendations. - 2️⃣ **Let users choose** what types of music they want to hear.| MCQ Topic | Connection to Computing Bias |
|---|---|
| 2.3: Extracting Information from Data | Bias can emerge when datasets are skewed or incomplete, leading to biased AI predictions and decisions. |
| 3.12: Calling Procedures | If biased functions or APIs are repeatedly used, the bias spreads throughout a system, such as facial recognition errors. |
| 3.17: Algorithmic Efficiency | Some efficient algorithms may prioritize speed over fairness, reinforcing biases in search engines or recommendation systems. |
| 5.1: Beneficial and Harmful Effects | Biased algorithms can offer personalized recommendations (benefit) but may also create filter bubbles and reinforce stereotypes (harm). |
| 5.2: Digital Divide | Bias in computing can worsen accessibility gaps, such as voice recognition software struggling with non-native accents. |
Questions to Ask About Bias (From CollegeBoard)
Enhancing or Intentionally Excluding
- Does the algorithm favor certain groups over others?
- Are specific perspectives or experiences being amplified while others are ignored?
- Is the data used to train the model diverse and representative of all relevant groups?
- Are accessibility and inclusivity considered in the design?
Intentionally Harmful/Hateful
- Could this system be used to spread misinformation or hate speech?
- Are there safeguards to prevent discrimination or harmful targeting?
- Who might be negatively impacted by the decisions of this technology?
- Is there a potential for reinforcing harmful stereotypes?
Receiving Feedback from a Wide Variety of People
- Have people from different backgrounds tested the system?
- Are there mechanisms in place to report bias or unintended consequences?
- How often is the system updated to address feedback and improve fairness?
- Are there specific efforts to include marginalized communities in testing and evaluation?
Homework Hack: Understanding Bias in Computing
Question:
Think of a system or tool that you use every day—this could be a website, app, or device. Can you identify any bias that might exist in the way the system works?
Task:
- Describe the system you’re thinking of.
- Identify the bias in that system and explain why it might be biased. (Is it Pre-existing Social Bias, Technical Bias, or Emergent Social Bias?)
- Propose one way to reduce or fix the bias in that system.
Example:
“I use a music app that suggests songs based only on what I already listen to. The system is biased because it limits me to a narrow selection of music. This is an example of Algorithmic Bias. To fix this, I would add an option for the app to recommend songs from different genres that I don’t normally listen to.”
🌟 Extra Credit Opportunity 🌟
Objective:
Complete the game to earn 100% and provide detailed explanations for each bias present in the game. For each bias, explain why it occurs and suggest a solution to eliminate or reduce its impact.
Task:
-
Play the Game
Play the provided game and aim to achieve 100% completion. Make sure to pay attention to the reasons that those biases are present. - Identify the Computing Biases:
As you play, take note of any of the following computing biases:- Pre-existing Social Bias: Biases that are inherited from society, such as racial, gender, or cultural biases, and are reflected in the system or game.
- Technical Bias: Biases that arise due to limitations in the technical aspects of the system, such as algorithmic or data limitations that result in unequal treatment of certain groups.
- Emergent Social Bias: Biases that develop during interactions between users or players within the system, such as crowd behavior or group dynamics that lead to unfair or unbalanced outcomes.
- Provide Explanations and Solutions:
For each bias you identify, explain why it is a bias and how it impacts our lives. Then, suggest at least one solution to address or minimize that bias. Solutions could include:- Altering code
- Introducing more diverse backgrounds
- Modifying the narrative or decision-making process
Example:
-
Bias: Technical Bias
Explanation: Amazon’s AI system has been found to favor male names and genders over female ones when making recommendations for job positions or skills training. This bias can limit opportunities for women or non-binary people.
Solution: Modify the training data to include a balanced and fair representation of genders. Reassess and retrain the AI to ensure that all gender identities have equal opportunity in the recommendation system, with checks in place to catch any skewed patterns. -
Bias: Pre-existing Social Bias
Explanation: A certain company’s AI algorithm recognizes faces more accurately for lighter skin tones, leading to biases in facial recognition systems. This can affect a person’s life or interactions, as the system might misidentify or exclude players with darker skin tones.
Solution: Improve the AI training data by ensuring it is diverse and representative of various skin tones. Ensure the facial recognition algorithm is tested across a wide range of skin tones and fine-tune it for accuracy across all demographics.
Extra Learning Links: Computing Bias
🌐 Websites
- Harvard: Algorithmic Bias – An overview of how bias appears in AI systems.
- Google AI: Fairness in Machine Learning – Google’s research and tools for reducing bias in AI.
- MIT Technology Review: The Fight Against Bias in Algorithms – Articles on bias in machine learning and AI ethics.
- AI Now Institute – Research on the social implications of artificial intelligence.
🎥 Videos
- CrashCourse: Bias in Computing – A short introduction to bias in algorithms.
- Coded Bias Documentary – A documentary exploring bias in facial recognition and AI.
- TED Talk: The Era of Blind Faith in Big Data Must End – Cathy O’Neil discusses algorithmic bias and its impact.
- AI for Good: Tackling Algorithmic Bias – Panel discussion on bias and fairness in AI.
📊 Academic References & Real-World Examples
📄 Definition and Information
- Nissenbaum et al. – Definition of computing bias.
- “Discerning Bias in Computer Systems” (Cornell Paper) – A research paper analyzing different types of bias in computing systems.
🔍 Real-World Examples
-
Amazon’s AI Hiring Tool (Pre-existing Social Bias)
Amazon’s AI system penalized resumes with words like “Women’s Chess Club.”
🔗 Read More -
Google Translate Gender Bias (Technical Bias)
Gender-neutral languages led to gendered assumptions in translation.
🔗 Read More -
Microsoft’s AI Chatbot Tay (Emergent Social Bias)
Tay absorbed and amplified harmful language from Twitter users.
🔗 Read More
🖥️ Interactive Resources
- Google’s What-If Tool – Experiment with bias in AI models.
- AI Fairness 360 (IBM) – A toolkit for detecting and mitigating bias in AI.
- MIT Media Lab: Moral Machine – An interactive tool exploring ethical decisions in AI.
- Algorithmic Justice League: Bias Detection Tools – Resources and interactive tools for identifying bias in algorithms.